EPR and Sustainability in Plastic & Flexible Packaging: A European Perspective
EPR and Sustainability in Plastic & Flexible Packaging: A European Perspective
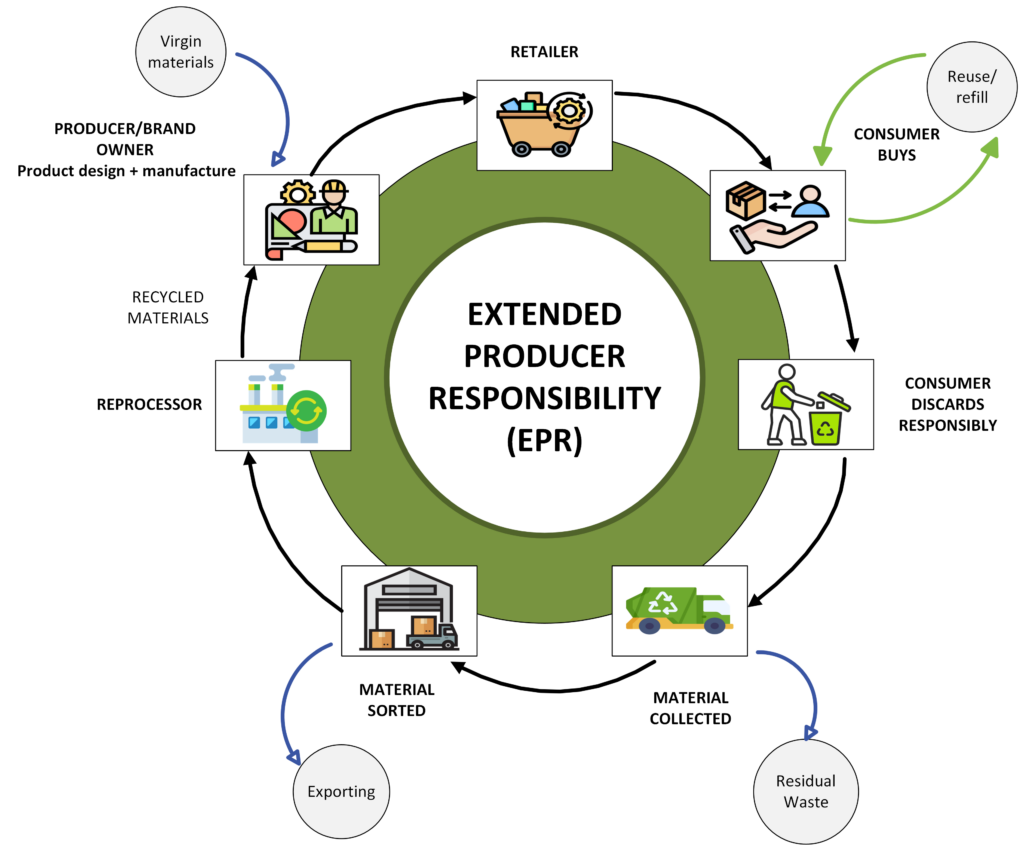
Across Europe, sustainability in retail packaging is no longer just a trend; it’s both a regulatory requirement and a consumer expectation. From personal care flexible packaging in Europe to food packaging flexible solutions in Europe, brands are under growing pressure to meet Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) targets while maintaining operational efficiency industries bodies like Flexible Packaging Europe are also driving awareness and setting benchmarks for sustainable practices. At the same time, the EU’s push for a circular economy in plastic packaging is reshaping the way manufacturers run their operations. Every stage of the packaging journey – from sourcing raw materials to recycling and final disposal – is now under the spotlight. Producers are under pressure to show transparency, cut down on waste, and provide reliable EPR reports. Delivering on all these demands is no straightforward job. Many companies in the flexible, plastic packaging sector in Europe face challenges in waste tracking, supplier data, customer transparency, and recycling compliance.
This is where Samadhan, with its ERP solution specific to Flexible and Film built on Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central and available on Microsoft AppSource, provides real value by embedding sustainability practices directly into business workflows. Below, we look at six major challenges packaging manufacturers face in Europe and how Samadhan’s ERP helps solve them.
1st Challenge: Lack of data on the amount of plastic waste generated during the production process
In Samadhan’s ERP solution, there is a feature to classify waste into recyclable and non-recyclable categories, each associated with a specific code. These broad categories are further broken into film type (blend) subcategories. While defining the recipe/formula for the film manufacturing process, these standard categories and subcategories are associated, so the generated waste can be easily recorded as per the pre-defined formula. The stock of these wastes, categorized and subcategorized, is recorded and visible for any further processes. Similarly, for other processes like printing, lamination, slitting, and converting, pre-defined waste categories and subcategories are used to maintain separate stock records at the end of each process.
2nd Challenge: Recognizing and recording recyclable items in material procurement from vendors (suppliers)
In many cases, vendors do not declare the items used for packing at the time of delivery. The packing materials entering the factory may fall into the following categories: Wood – pallets, wooden boxes, crates, etc.
- Plastic – shrink wrap, outer packing, pallets, strings, tapes, etc
- Metal – support rods, nails, screws, corners, etc.
- Paper – including corrugated boxes, sheets, wraps, and pallets.
- Foam – foam structures, pads, etc.
Samadhan’s solution addresses this by predefining all categories and subcategories in the ERP. Recording the quantity (by weight or numbers) at the time of receipt, if details are provided. Where vendors do not provide information, the materials are counted or weighed and recorded in the system initially. Over time, vendors are educated about this requirement, so accurate data can be captured consistently.
3rd Challenge: Informing customers about packing materials at the time of delivery
The waste categories defined for purchase are also used for dispatches to customers. Quantities are automatically calculated based on packing instructions provided by customers. The system allows five levels of packing (shrink wrap, bundle, small carton, master carton/case, pallet) to be defined, ensuring accurate calculation of each packing type at the time of dispatch/invoicing. This ensures customer sustainability requirements are fully met.
4th Challenge: Recycling waste where recycling facilities are available
With Samadhan’s solution, accumulated recyclable waste can be further processed into granules/pellets. The recycled granules or pellets are blended back into the formula for producing plastic films.
5th Challenge: Safe and efficient disposal of non-recyclable waste from the facility
All non-recyclable waste is quantified and logged within predefined locations in the system. This waste is removed by selling it to authorized parties as required. Since every removal is recorded in the system, manufacturers always gain clear visibility of waste movement.
6th Challenge: Providing accurate data for EPR reporting
The EPR regulations are evolving, and reporting requirements vary from one country to another. In order to overcome the challenge, all waste data, including quantities, sources, and destinations, is exported at the click of a button so that reports are prepared according to the required format for reporting.
The closing thoughts
Europe is moving quickly towards tougher recycling and waste-reduction goals, and packaging companies need systems that balance day-to-day efficiency with sustainability compliance. From managing flexible pouch packaging in Europe to tracking high-barrier films for food safety or responding to growing demand for retail packaging sustainability in Europe, Samadhan ERP gives manufacturers the visibility and control to stay ahead. With built-in tools for waste tracking, supplier accountability, customer transparency, recycling integration, and reporting, Samadhan doesn’t just help companies meet EPR rules; it helps them work smarter, cut inefficiencies, and strengthen trust with their customers. EPR compliance may look complex on paper, but the first step is often as simple as looking at the right solution for your business.
